Transarterial Chemoembolization
Chemoembolization is a minimally invasive treatment for cancer that can be used when there is too much tumor to treat with radiofrequency ablation (RFA), when the tumor is in a location that cannot be treated with RFA, or in combination with RFA or other treatments.
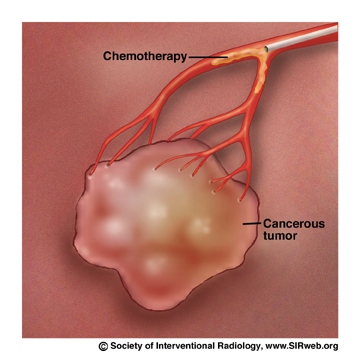
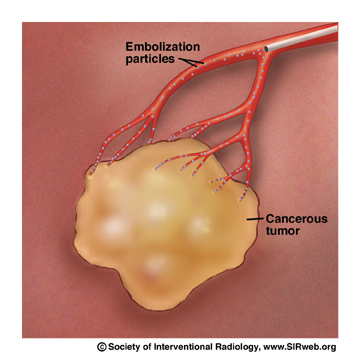
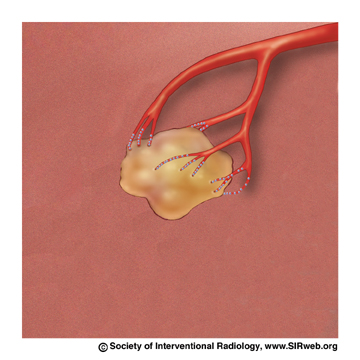
Chemoembolization delivers a high dose of cancer-killing drug (chemotherapy) directly to the organ while depriving the tumor of its blood supply by blocking, or embolizing, the arteries feeding the tumor. Using imaging for guidance, the interventional radiologist threads a tiny catheter up the femoral artery in the groin into the blood vessels supplying the liver tumor. The embolic agents keep the chemotherapy drug in the tumor by blocking the flow to other areas of the body. This allows for a higher dose of chemotherapy drug to be used, because less of the drug is able to circulate to the healthy cells in the body. Chemoembolization usually involves a hospital stay of two to four days. Patients typically have lower than normal energy levels for about a month afterwards.
Conditions treated include cancer of the Kidney, Liver and Lung.